A New Frontier in Breast Cancer Treatment
presented by: Menova
1. Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer
![]()
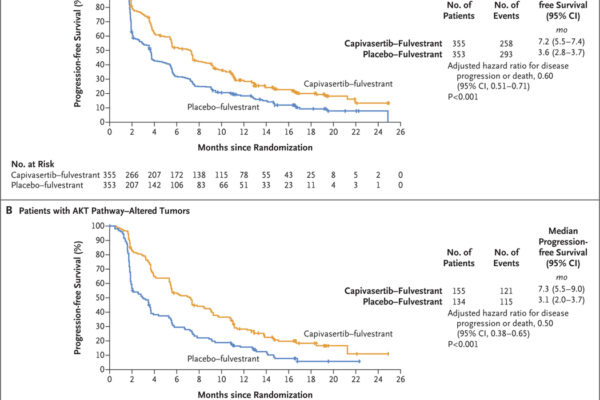
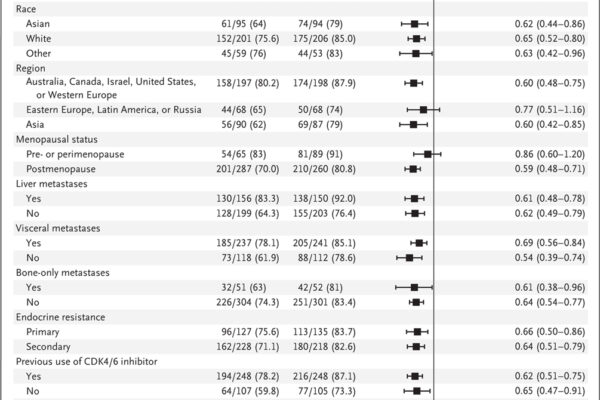
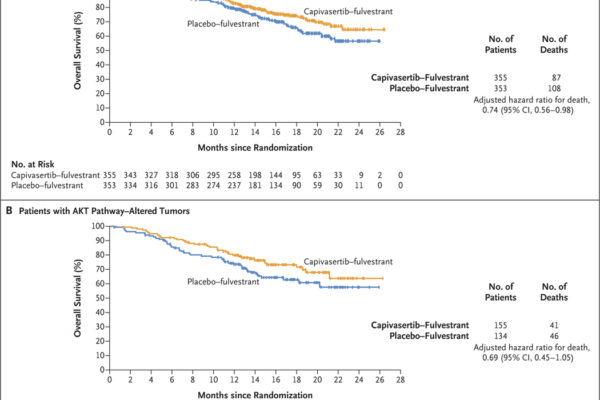
A phase 3 trial assessed capivasertib combined with fulvestrant in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. The combination significantly improved progression-free survival compared to placebo plus fulvestrant, with notable benefits in patients harboring AKT pathway alterations.
This trial investigated the efficacy and safety of capivasertib in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either capivasertib plus fulvestrant or placebo plus fulvestrant.
The results demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival for patients treated with capivasertib plus fulvestrant, particularly in those with tumors harboring alterations in the AKT pathway. However, the treatment was associated with increased rates of adverse events, primarily rash and diarrhea.
2. Capivasertib Plus Paclitaxel as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: The PAKT Trial
![]()
This randomized phase 2 trial evaluated capivasertib with paclitaxel versus placebo with paclitaxel in untreated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. The addition of capivasertib led to improved progression-free and overall survival, especially in patients with PI3K/AKT pathway alterations.
The PAKT trial investigated the efficacy and safety of adding the AKT inhibitor capivasertib to standard first-line paclitaxel chemotherapy for patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The study found that the combination therapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to paclitaxel alone. The benefit was particularly pronounced in patients with tumors harboring alterations in the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway. While the treatment was generally well-tolerated, it was associated with increased rates of adverse events, primarily diarrhea and rash. These findings suggest that capivasertib may be a promising therapeutic option for TNBC, especially in patients with specific genetic alterations.
3. The Emerging Role of Capivasertib in Breast Cancer

A comprehensive review highlighted capivasertib’s potential across breast cancer subtypes, emphasizing its efficacy in tumors with aberrant PI3K/AKT signaling. Ongoing trials are further exploring its role in combination therapies.
The PI3K/AKT pathway is frequently activated in breast cancer, making it a promising therapeutic target. Capivasertib, a novel pan-AKT inhibitor, has shown significant preclinical activity against breast cancer cells, particularly those with PIK3CA or MTOR alterations. Clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of capivasertib in combination with other therapies, such as fulvestrant, paclitaxel, and olaparib. While the most common side effects include hyperglycemia, diarrhea, and rash, these are generally manageable. Ongoing Phase III trials are evaluating the role of capivasertib in various settings of breast cancer, aiming to further solidify its position as a valuable treatment option.
4. Effect of Capivasertib in Patients With an AKT1 E17K-Mutated Tumor: NCI-MATCH Subprotocol EAY131-Y Nonrandomized Trial

This nonrandomized trial focused on capivasertib’s activity in patients with tumors harboring the AKT1 E17K mutation. The study reported a modest overall response rate, suggesting limited single-agent activity in heavily pretreated populations.
The NCI-MATCH trial evaluated the efficacy of capivasertib, a pan-AKT inhibitor, in patients with metastatic tumors harboring the AKT1 E17K mutation. This non-randomized study enrolled 35 patients with various cancer types, including breast, gynecologic, and others. The primary endpoint, objective response rate (ORR), was 28.6%, with one complete response and several partial responses observed. Additionally, a significant proportion of patients experienced stable disease. While capivasertib was generally well-tolerated, common side effects included hyperglycemia and rash. These findings suggest that capivasertib may be a promising therapeutic option for patients with AKT1 E17K-mutated tumors, particularly in the setting of limited treatment options.

Find out if TRUQAP could be right for your patients.
TRUQAP is for people with HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer who test positive for abnormal PIK3CA, AKT1, and/or PTEN genes
Take Control NowCapivasertib: Advancing Breast Cancer Treatment
Capivasertib, an oral AKT inhibitor, has demonstrated significant efficacy in various breast cancer subtypes, particularly those with PI3K/AKT pathway alterations. Clinical trials have shown that combining capivasertib with standard therapies enhances progression-free and overall survival in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ongoing research continues to define its role in targeted cancer therapy, offering hope for more effective and personalized treatment options.